
When God means to punish a man He sends him stupid friends and clever enemies.
Joe Abercrombie, Best Served Cold
Introduction
Gentle Readers are probably familiar with the modern mass-produced mass-marketed exchangeable-blade handsaws made in Japan. In this first part of a two part series we will briefly examine the history of how these saws came to be, how they are manufactured, and the market forces that made them so popular in Japan and even overseas.
In Part 2, to be published later, your most humble and obedient servant will list pros and cons and share some techniques for improving their performance.
Gentle Reader may already be aware of these saws and even own and use them at work daily, but in this article your humble servant will share details about them not available elsewhere. I pray it proves informative, or at least entertaining.
Terminology
In the Japanese language the type of consumer-grade handsaw I mentioned above with blades that can be removed and reattached to a handle mechanism are called “kaeba nokogiri” (kah/eh/bah nokogiri 替刃鋸) meaning, of course, “exchangeable-blade saw.” From this point forward I will call them “kaeba saws” for brevity. They have entirely replaced traditional forged handsaws in Japan for good and valid reasons, and indeed are popular throughout Asia as well as Western countries too.
So let’s begin this adventure by considering the history of this new version of an old tool that shook the handsaw world like a terrier does a rat.
Historical Background
In the late 1970’s the kaeba handsaw appeared in the Japanese market changing everything.
I’m not sure who first developed the concept, but there’s no doubt it was inspired by the convenient and highly-profitable bits and blades used with powertools. The first automated equipment for making these sawblades was developed by a 150 year old company located in Sanjo, Japan that shifted their traditional saw sharpening business to producing and selling CNC saw sharpening machines. Later, inspired by automated circular-saw blade production techniques, they went on to develop CNC machinery to fabricate handsaw blades in an automated production line.
Production Methods
The manufacturing process begins with materials, of course. The primary material is pre-hardened sheet steel sanded to uniform thickness in rolling mills, and delivered to the blade manufacturer in large, heavy rolls. This product means the blade manufacturer doesn’t have to sort, forge, heat-treat, stress-relieve, or taper-grind the steel. In fact, he couldn’t even if he wanted to.
As this roll of sheet steel is unspooled into the production line, CNC machines cut and deburr the blade blanks, punch the teeth, and shape and sharpen them with special abrasives, after which set is applied by machine. And unlike traditional hand-forged fixed-blade saws, the plates are not forged, taper-ground or heat treated by the saw manufacturer at all. This is an important distinction to those who know saws from shinola.
Some but by no means all such blades are tensioned between two steel rollers in imitation of the techniques used during the manufacture of circular saw blades.
Most kaeba manufacturers induction-harden just the tips of the teeth of some blades for extra durability as the blades are fed between, and instantaneously heated red hot by, electrically-charged copper blocks, then immediately quenched in coolant spray after exiting the induction blocks leaving them a darker oxidized color. These blades cannot be sharpened by hand as the teeth are harder than files.
Handles
Kaeba saw’s handles are sometimes made of wood, sometimes of plastic, and sometimes of rubber over plastic. The blade is secured to the handle by metal mechanical widgets and sometimes screws integral to the handle. The blades can be quickly and easily changed encouraging consumers to do so frequently, but each manufacturer’s blades will fit only their proprietary handle locking the consumer into buying proprietary replacement blades, much like printers and ink/toner cartridges, because as the O’Jays sang on Soul Train, it’s the blade that makes the money, money, money, money, mo-ney, but it’s the handle that drives market share.
And with labor costs to produce such a handsaw a single digit percentage of what’s required for a traditional handsaw, the few manufacturers of kaeba saws find it difficult betimes to wade through the mountains of mad stacks laying about.
With the production technology perfected, compatible materials available, and CNC machinery in the hands of a few manufacturers, it was only a hop skip and a jump to widespread sales of kaeba handsaws, and if I may paraphrase my old carpenter foreman Uglúk, it looks like rats are back on the menu, boys.
Some prefer their rodent roasted on rye with horseradish sauce, but I prefer mine sauteed with a drop o’ Tabasco Sauce, or as Bert suggested, maybe even a floater for delicately piquant flavor! What about you?
The Societal Impacts of Kaeba Handsaws 替刃鋸の波及
I mentioned above that this new type of saw changed everything. Of course, that’s a bit of an exaggeration because babies still love boobies and politicians graft, but indeed some things changed drastically in Japan.
The first big change the kaeba handsaw wrought was putting nearly all the traditional sawsmiths in Japan out of work in a matter of a few decades. Indeed, the number of sawsmiths still forging traditional saws full-time nowadays can be numbered on the fingers of one hand after a manicure using a tablesaw.
The second domino was the near destruction of the saw handle industry. As the demand for exchangeable-blade handsaws ramped up, the production of traditional handsaws, along with the need for traditional handles, crashed.
You see, exchangeable-blade saws have patented brand-specific wooden handles with integral metal mounting plates/screws/clips to which the specific blade-maker’s replacement blade is attached. The maker of each brand of exchangeable-blade handsaw subcontracts the production of their handle to specific suppliers, and since the producers of handsaws are now few, so are the handle suppliers. Sadly, your humble servant is aware of only one, and occasionally two producers of traditional handles still operating. I believe they still have all their fingers but I’m concerned one gentleman’s liver has seen better days.
Just when it looked like things couldn’t get worse, the third domino fell-over and crushed the saw sharpening trade. While many kaeba saws can be resharpened, some cannot be economically resharpened at all because their teeth are induction-heat-treated to be harder than sawfiles. In fact, while it’s usually a little cheaper to have even a kaeba sawblade professionally sharpened rather than purchasing a replacement, buying a new sawblade and tossing the old one is quicker, more convenient and obviates the need to carry spare saws to a jobsite because thin, lightweight replacement sawblades will suffice. In any case the jobs of saw sharpeners (metateshi meh/tah/teh/she 目立て師), like those of sawsmiths, handlemakers, wheelwrights, and honest climate scientists have been practically eliminated.
The one overarching societal lesson one can take away from this is that technological advances always have and always will engender painful changes in every industry in the world, and the case of the Japanese handsaw industry only confirms that one can either ride the train of technology sipping tea and eating pringles in comfort as it rolls along, or grease the tracks as it runs one over. Just ask the once mighty Eastman Kodak company of camera and film fame if ‘taint so.
A similar progression occurred within the saw manufacturing industry in the West, but instead of the changes stemming from product innovation, the causes were quality adulteration, active neglect of customers needs, and abandonment of unparalled tradition. Welcome to the Harvard School of Business Management’s model of “profit through disruption” in action. I hear they’re looking for a new university president.
An American Handsaw Maker
To this point we’ve taken a shallow look at Japanese handsaws, especially the impact of the kaeba variety on Japanese markets, but highly intelligent Gentle Readers (could there possibly be any other kind? absolutely not!) may wonder how in heck these strange Japanese products managed to make such profound inroads into Western markets, so a few points about a well-known American saw manufacturer may prove instructive.

Gentle Reader may recall that the famous American handsaw manufacturer Henry Disston (1819–1878) was born in England the son of a designer and manufacturer of lace-making machines and immigrated to the USA in 1833 along with his father and sister. His father died three days after stepping off the boat. Tough luck.
Being a determined and diligent young man, Henry apprenticed himself to a saw company in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. In 1840 he went independent, and after some lean years building a reputation for quality, he founded the Keystone Saw Works there in 1850. After the American civil war his son Hamilton joined the business and Henry changed the company’s name to Disston & Son, and later to Disston & Sons. At its peak Disston & Sons was the largest and most productive saw manufacturer in the world with 8,000 direct employees working on 300 acres.


At the time he established the Keystone Saw Works, nearly all tool steel used in North America was imported from Great Britain. This was a serious impediment to growth so Henry established the first crucible steel mill of consequence in the Americas to supply steel for his products and to support the war effort, and although other more famous, ruthless individuals falsely took credit for developing steel production in America, they were originally only Henry’s customers. For the next 25 years, the Disstons were among the largest producers of quality tool steel in the world outside England.
Interestingly, American consumers at the time were absolutely convinced that only Birmingham, England could make quality tool steel, so while other American sawmakers imported their steel from England, D&S used their own steel, avoiding the high import tariffs of the time. But to avoid the stigma of being seen as a “colonial product,” for many decades the acid-etched engraving on Disston & Sons’ sawblades included variations of the words “London Spring Steel” intimating that more prestigious British steel was used. Interestingly modern chemical analysis suggests that D&S’s tool steel was at least as high-quality as that imported from Britain at the time.


The first handsaw I owned as a young man was an antique and terribly rusty D&S D-8 thumbhole rip saw missing a handle (but with partial screws) I found languishing in a joint compound bucket in the back of a Las Vegas pawnshop. My penny-pinching carpenter father said it could be restored to be a better saw than I could buy new, and at $3 and a lot of elbow grease, the price was right and so was he. After derusting the blade, making a handle from a piece of scrap walnut, and reworking the teeth several times until I got the nack, that antique D-8 became an excellent handsaw, far superior to the new Disston saws still available at the time. My son owns it now.

The first point I want to make in this section is that by the time I was old enough to want to own a handsaw, the circular saw ruled the construction industry in the West (but not yet in Japan) and most younger carpenters neither owned a decent handsaw nor could care less. As a result of these market changes, the production and sale of handsaws became less profitable, the quality of those available became shamefully degraded, and instead of increasing production efficiency, and/or innovating like Japanese saw companies did, D&S did a double doodoo on quality, then lay down to be eaten by vultures. Other than a few tiny, recently-established boutique backsaw makers, the once-mighty American handsaw industry is now as dead as decency.
My second point is that this shameful degradation and subsequent abandonment of a once huge and profitable American industry fomented despair among Western woodworkers who needed quality handsaws but couldn’t procure them new anymore forcing many, like your humble servant, to haunt flea markets, pawnshops, and later Ebay for old handsaws (including Disston & Sons products) and to even purchase tools imported from Japan back when Japan’s reputation for quality was not as shiny as it is now. These forsaken and “disrupted” woodworkers, hungry for better tools, were the primary reason medium-quality but very sharp Japanese crosscut handsaws first became so popular in the USA. And when Japanese kaeba saws became available later, overseas markets snapped them up like the proverbial duck on a June bug.
FYI, the Disstonian Institute website has some interesting information about Disston & Sons those interested in history may enjoy.
As an aside, I noticed that Disston, now the Chinese holesaw maker, is offering a newer version of the D-8 26″ swayback rip/crosscut handsaw exclusively on Amazon. It looks shiny! The country of manufacture and local content is not listed anywhere, but probably not the USA and definitely not Philly. The video on their website almost made your unworthy servant spew chunky chunks. Consider yourself warned.
Let us next shift our attention back to the kaeba saw and consider the first and most popular such handsaw, as well as some other popular varieties.
Dozuki Kaeba Handsaw
The dozuki handsaw was the first Japanese kaeba saw to become popular overseas, perhaps initially attracting attention because it vaguely resembles the petite “gents” back saws once popular with amateurs. The dozuki is a thin crosscut backsaw (a single-edged handsaw with a steel or brass stiffener attached to its back) that cuts on the pull stroke.
The name is pronounced dough/zoo/key and is comprised of two Chinese characters: “胴” pronounced “dough” meaning “trunk” as in the trunk of a tree or the human torso, and 付き pronounced “zookey,” a verb meaning “to attach or make.” To the best of your humble servant’s understanding most Western woodworkers are unaware of the name’s meaning or the saw’s specialized purpose but nonetheless they use them for everything but spreading jam on toast (marmalade gums up the teeth terribly). The name refers to the job of cross-cutting the shoulders of tenons, but not the cheeks, which is a job for the specialized “ hozohiki” rip saw.

In the case of joinery, furniture, cabinetry, and fine architectural woodwork, well-made mortise and tenon joints are essential to the appearance and even the strength of the finished product. And since the shoulder is the only visible part of most mortise and tenon joints, shoulder appearance is important.
Cutting tenon shoulders in a craftsman-like manner in the Japanese tradition demands not only a good eye, a good saw, and a skilled hand but speed, because the craftsman is expected to saw deftly, precisely and cleanly to the layout line the first time every time, all day long. This differs from the inefficient, amateurish methodology for cutting tenons in cabinetry and joinery as taught by the Holy Masters of Woodworking in the West who lack adequate saws and/or skills and shamefully advocate cutting wide of the layout line and sneaking up on it with chisels and planes. How embarrassing.
A quality dozuki saw is extremely effective at making these cuts. To do so it must be able to make a straight, precise, smooth cut right to a final layout line every time without wandering off into the weeds and without having to use a paring chisel or shoulder plane to obtain a clean, square, straight shoulder. Accordingly, it must have a thin, true plate that won’t produce excess friction, nor buckle, oil-can, or bind as it heats up, and fine, uniform teeth with minimum practical set. It must also have a lightweight but rigid steel back that effectively keeps the blade’s plate true, protects it from buckling, and discourages it from weedy adventures.
Kaeba dozuki saws come in various lengths ranging from 150mm to 240mm. TPI varies with maker. Zetsaw by Okada Industries is my favorite kaeba brand and makes some with induction-hardened teeth that can be made extremely useful with the modifications I will share in Part 2. FYI, your humble servant does not sell Z-saws and has never received free (or even discounted) samples, nor been wined, dined laid or paid to promote them.

Interestingly, even before the development of the exchangeable-blade kaeba saw, the Japanese dozuki saw was used in the West for cutting dovetails, a job which requires occasional crosscuts but frequent rip cuts, something the hozohiki saw does much better. In any case, that Western woodworkers ended up preferring the Japanese dozuki saw for even rip cuts may give Gentle Reader an idea about the comparatively adulterated performance of readily-available Western dovetail saws from the 1970’s onward.
The kaeba concept has been expanded to include useful saws of many shapes and sizes, some of which your humble servant owns and uses, especially when there is a risk of damaging one of his professional-grade fixed-blade handsaws.
Let’s next consider some popular varieties of kaeba saws other than the dozuki and hozohiki.
Kaeba Crosscut/Rip Saws
The best selling Japanese handsaw both domestically and internationally is the standard single-edged (“kataba”) carpenter’s crosscut saw. These come in various lengths, shapes, and with various types of teeth. They are handy in the shop, and I always have one or two of these on hand when working in the field, especially when cutting EWP (engineered wood products) which I refuse to allow my hand-forged saws to even touch no matter how much they wiggle and whine. If you need to cut plywood or other EWP, these saws are a must-have IMHO. More on this subject in Part 2.


But the usefulness of kaeba saws is not limited to woodworking and sandwich making only, oh no. I carry a 333mm (13″) kaeba formwork saw with a lightweight plastic pistol-grip handle when hunting because no other tool I know of is so light, so compact, and can cut so much wood so quickly.

The Silky brand arborist’s saw blades are excellent for this purpose too if you ditch the heavy rubber handle and gaudy scabbard.
Ryouba Double-edged Kaeba Saws
This style of kaeba saw combines a rip saw and a crosscut saw in one exchangeable blade. I own one 270mm kaeba ryouba saw with induction-hardened teeth I like well enough, but I still prefer fixed-blade ryouba saws. I daresay most people can’t tell the difference.


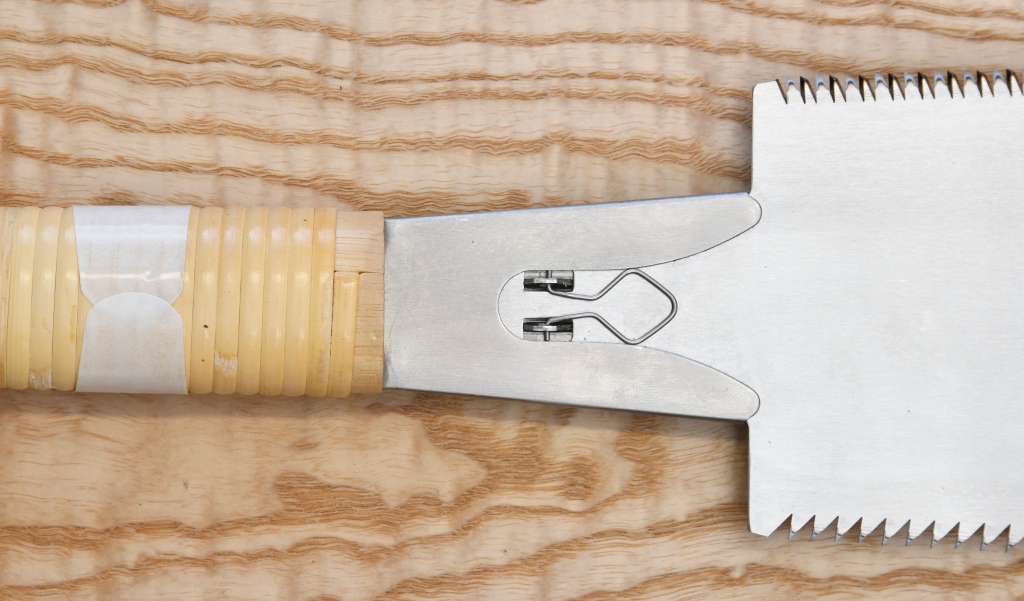
Saws retailers here in Tokyo tell me that sales of kaeba ryouba saws have dropped off dramatically the last few years probably due to increased prefabrication and LGS metal studs replacing wood and LVL (laminated veneer lumber) framing for interiors such that rip cuts in wood in the field are seldom necessary. I believe this increase in the use of pre-manufactured components is in part due to three inter-related factors: (1) Rising construction costs; and (2) High demand in the construction industry; and (3) An aging workforce resulting in a decrease in available manpower in the construction industry making it difficult to meet customer demand. I fear the current attitude of Japanese women about bearing and raising children will prove disastrous for the nation soon as you can say “Bob’s not your uncle.”
Teflon Coated Blades
Zetsaw sells some of its blades with a PTFE teflon coating which I have found to be very effective in reducing friction and preventing sap from accumulating when cutting some softwoods. Makes a great egg turner too.

The Adventure Continues
In the next installment in this operatic series about the funky love of money, fine dining and handsaws we will examine the advantages and disadvantages of kaeba saws compared to traditional fixed-blade saws, and explain simple techniques Gentle Reader can employ to supercharge your kaeba saws.
But in the meantime, since the IMF, EU and UN are on the verge of outlawing backyard vegetable gardens at the same time they are taking by force and sacrificing the land of European farmers on the alter of the religion of “Climate Change,” (how did that work out for Sri Lanka?) all while increasing pressure on others (regular people, but not the bureaucrats/elite) to substitute bugs for meat (I kid thee not), I would appreciate Gentle Reader sharing any tasty recipes you may have for crispy, crunchy low-fat rodent dishes in the comments below. I need to broaden my culinary repertoire in preparation for more societal “disruption,” you see.
YMHOS

If you have questions or would like to learn more about our tools, please click the “Pricelist” link here or at the top of the page and use the “Contact Us” form located immediately below.
Please share your insights and comments with everyone by using the form located further below labeled “Leave a Reply.” We aren’t evil Google, fascist facebook, thuggish Twitter, or the son of a President and so won’t sell, share, or profitably “misplace” your information. If I lie may my dozuki saw wander like a clowder of kittens.
Leave a comment